上 unit of gravitational constant g 213091-What is the si unit of gravitational constant g class 9
· Because we know the units for G are m³ / kgs², there must be a per unit volume component in this last formula and given that ρV = mass;The gravitational force F between two bodies of mass m1 and m2 at a distance R is In SI units, G has the value 667 × 10 11 Newtons kg 2 m 2 The direction of the force is in a straight line between the two bodies and is attractiveThe gal (symbol Gal), sometimes called galileo after Galileo Galilei, is a unit of acceleration used extensively in the science of gravimetry The gal is defined as 1 centimeter per second squared (1 cm/s 2) The milligal (mGal) and microgal (µGal) are respectively one thousandth and one millionth of a gal
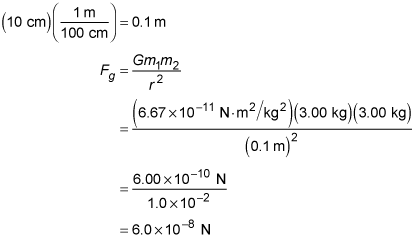
Gravitational Force In Physics Problems Dummies
What is the si unit of gravitational constant g class 9
What is the si unit of gravitational constant g class 9- · The Newtonian gravitational constant, G, is one of the most fundamental constants of nature, but we still do not have an accurate value for itSI unit of gravitational force is kg m/s^2 but newton tell us about this first time so for his credit and his respect SI system gives their name as an unit of gravitational force So the unit is Newton




Imgv2 1 F Scribdassets Com Img Document
Planck's constant h, speed of light c and gravitational constant G are used to form a unit of length L and a unit of mass M Then the correct option (s) is (are) Physical World, Units and Measurements 2 Two independent harmonic oscillators of equal mass are oscillating about the origin with angular frequencies ω 1 and ω 2 and have total · Hi Part of my homework was to work out what the SI base units of the gravitaional constant are I'm crap at working out base units so could somebody help me out? · "Golly, G!" "For any two masses, be they bowling balls or planets, the gravitational force between them is determined by their masses, their distance and the number G," says Mack Thanks to experiments conducted by Henry Cavendish in the 1790s, we now know the gravitational constant has the numerical value of around 667 x 10 11 Newtons (m2/kg2)
96 · Gravitational constant G (85)8 cm 3 g1 s2 128 Electron charge e (14)10 esu 030 Mass of electron SYMBOL NUMBER EXP CGS UNITS Astronomical unit AU 1496 13 cm Parsec pc 3086 18 cm Light year ly 9463 17 cm Solar mass M o 199 33 g Solar radius R o 696 10 cm Solar luminosity L o 39 33 erg s1 SolarGravitational constants G x 1011 m 3 kg1 s2 x 1012 cm 3 g1 s2 x 109 ft 3 lb1 s2 standard gravity g o m s2 cm s2 ft s2 gravitational conversion factor g c m kg kg f1 s2 cm g g f1 s2 ft lb lb f1 s2 Planck constant h x 10Gravitational Constant (G) = F × r 2 × Mm1 Or, G = M 1 L 1 T 2 × L 2 × M 2 = M 1 L 3 T 2 Therefore, the gravitational constant is dimensionally represented as M 1 L 3 T 2
· G = 6673×10 11 N m 2 kg 2 It is typically used in the equation F = (G x m 1 x m 2) / r 2 , wherein F = force of gravity G = gravitational constant m 1 = mass of the first object (letsNewton's gravitational constant must be gravitational acceleration multiplied by an area per unit mass ie G = aₒc² / mᵤ {m³/kg/s²} where Fᴺ = Newtonian force between a proton and an electron Fᴾ = Planck's force V p = volume of a proton · Click here 👆 to get an answer to your question ️ SI unit of universal gravitation constant 'G' is Parmeshwar007 Parmeshwar007 Physics Secondary School SI unit of universal gravitation constant 'G' is 2 See answers HbMarvel HbMarvel Answer Nm² is the SI Unit of Gravitational constant prachi6133 prachi6133 Answer




What Is Difference Between G And G
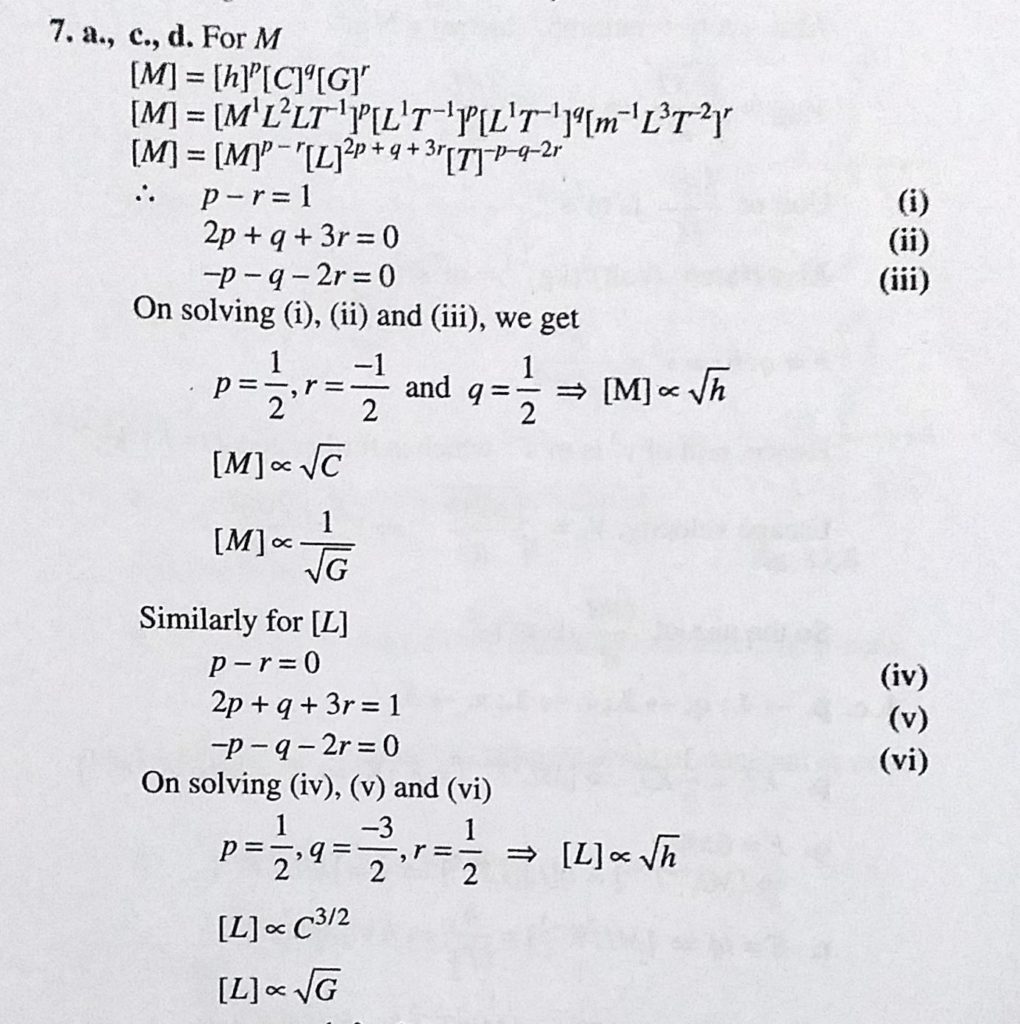



Planck S Constant H Speed Of Light C And Gravitational Constant G Are Use To Form A Unit Of Length L And A Unit Of Mass M Then The Correct Options Is
The numerical value of gravitational constant G is 667×10−11N m2kg−2 The SI unit of G is N m2kg−2 Answer verified by Toppr Upvote (0)There is no equation per se It can be arrived at by dimensional analysis From F = m a ;The Gravitational constant (G) was derived after deriving the gravitational coupling constants for the electron (α Ge) which is explained here Classically, the coupling constant is the ratio of gravitational force of two particle masses versus the electric force of two particle charges But this doesn't describe what it truly is




Gravity Of Earth Wikipedia




C H A P T E R 4 Forces And Newton S Laws Of Motion Ppt Video Online Download
The formula to convert G to $ is 1 Gravitational Constant = 1 US Dollar G is 1 times Smaller than $ Enter the value of G and hit Convert to get value in $ Check our G to $ converter · F = G M 1 M 2 / d 2 (1) Unit of Gravitational Force N or Newton Here, G is called the universal gravitational constant It is an empirical physical constant, which has a value of 667 X 1011 Nm 2 /kg 2 Its dimensional formula is M1 L3 T2This is equivalent to length cubed, divided by mass and by time squared In SI base units, this amounts to meters cubed per kilogram per second squared In cgs, G can be written as G ≈ 6674×10−8 cm3⋅g−1⋅s−2




Newton S Law Of Universal Gravitation Is R Clutch Prep




C H A P T E R 6
The gravitational constant (G) first appeared in Newton's gravity equations, and later in Albert Einstein's equations for general relativity Force is related to mass and the distance between objects, but G remains the constant in Newton's force equation · Weight and the Gravitational Force The constant of proportionality, G, is the universal gravitational constant The gravitational constant denoted by letter G, is an empirical physical constant involved in the calculation(s) of gravitational force between two bodies 0000 15 x 1011 m3 kg1 s2 6674 30 x 1011 m3 kg1 s2 · The dimensions assigned to the gravitational constant are force times length squared divided by mass squared;




If G Is Universal Gravitational Constant And G Is Acceleration Due To Gravity Then The Youtube




Newton S Law Of Gravitation Statement Explanation Problems
Gravitational force between two objects of mass m 1 and m 2 separated by a distance r, F = r 2 G m 1 m 2 G = m 1 m 2 F r 2 SI unit of universal gravitational constant G is K g 2 N m 2 · A slug is 322 lbm Slug is really the mass unit you want to use if you want F = ma to give you the force in lbf One lbf is the force you need to exert on a mass of 1slug to give it an acceleration of 1 ft/sec 2 If you exert a force of 1 lbf on a 1 lbm, its acceleration will be 322 ft/sec^2 Feb 9, 14Write the Numerical Value of Gravitational Constant G with Its SI Unit CISCE ICSE Class 9 Question Papers 10 Textbook Solutions Important Solutions 5 Question Bank Solutions Concept Notes & Videos 242 Syllabus Advertisement Remove all ads Write the Numerical Value of Gravitational Constant G with Its SI Unit




Value Of Gravitational Constant In Cgs System Youtube




Fill In The Blanks Value Of Gravitational Constant G On Moon Is As On Earth
As f(r) varies inversely as a square of 'r' it is also known as inverse square law force The proportionality constant (G) in the above equation is known as gravitational constant The dimension formula of G is M1 L 3 T2 Also, the value of the gravitational constant, In SI units 667 × 1011 Nm 2 kg2, In CGS units 667×108 dyneThe nominal "average" value at Earth's surface, known as standard gravity is, by definition, m/s 2 This quantity is denoted variously as gn, ge (though this sometimes means the normal equatorial value on Earth, m/s 2 ), g0, gee, or simply g (which is also used for the variable local value)Thanks If anyones wondering, G is 667 x 10ˉ¹¹ N m² kgˉ²




Difference Between G And G Scholr




Gravitational Fields Newton S Universal Law F Mm F 1 R 2 What Are The Units Of G The Universal Gravitational Constant G X Nm 2 Kg Ppt Download
SI Unit Universal Gravitational Constant G Gravitational Constant is an empirical physical constant that is involved in the calculation of gravitational effects in Newton's Law of Universal Constant Constant at any point in this universe G = ×1011 Nm 2 /kg 2 L 3 M1 T2 Nm 2 /kg 2 · The SI unit of G is 667×1011 kg1 m 3 s2Its value remains constant at anywhere in the universe this is the reason it is a universal constant Its existence comes as proportionality constantDyn = g cm/s/s (in cgs) N = 1000 g 100 cm/s/s = 100,000 gcm/s/s = 100,000 Dyn So a Newton is 100,000 Dyn G is 6




Gravitational Force Flip Ebook Pages 1 35 Anyflip Anyflip




Section 2 Newton S Law Of Gravitation Ppt Video Online Download
· Unit and Value of G (Universal Gravitational Constant or Gravitational constant) In the equation of gravitational force, G is a constant, called Universal Gravitational Constant or Gravitational constant Its unit is Nm2kg2 And the Value ofUniversal Gravitational Constant = Force × r 2 × m 1 × m 21 Or, G = M 1 L 1 T 2 × M 0 L 1 T 0 2 × M 1 L 0 T 0 1 × M 1 L 0 T 0 1 = M 1 L 3 T 2 Therefore, the Universal Gravitational Constant is dimensionally represented as M 1 L 3 T 2G to Percentage The formula used to convert G to Percentage is 1 Gravitational Constant = 1 Percentage Measurement is one of the most fundamental concepts Note that we have Fahrenheit as the biggest unit for length while Per Degree Celsius is the smallest one




What Is The Value Of Gravitational Constant Value Of Capital G




A Suitable Unit For Gravitational Constant Is Youtube
G is the universal gravitation constant, aka Newton's constant It is approximately 6674×10−11 m3⋅kg−1⋅s−2 g is the acceleration due to gravity, and is approximately 981 m⋅s−2 On the other hand, if you mean what do G and g mean in SI, G is a prefix meaning 10^9, and is spelt GigaF = GM1M2 d2, where F is the gravitational force between two point masses, M1 and M2;Then calculate the gravity store increase (the gravitational potential energy), remembering that g is 10 N/kg on Earth gravitational potential energy = mass × height × gravitational field strength




If The Unit Of Length Be Doubled Then The Numerical Value Of Universal Gravitational Constant G Will Brainly In




Si Unit Of G Is Nm 2kg 2 Which Of The Following Can Also Be Used As The Si Unit Of G
D is the distance between M1 and M2;Units in gravitational constant I was reading on the internet and I found that the gravitational constant is roughly 6674 × 10 − 11 m 3 k g − 1 s − 2 I also found thatIn physics, the value of capital G (gravitational constant) was initially proposed by Newton A 667 * 106 cgs unit B 667 * 107 cgs unit C 667 * 108 cgs unit D 667 * 1010 cgs unit 16 Election Results By County Github, Bunk'd Season 1 Episode , Don Quixote Film Adaptations, Say Say Say, In CGS (centimetergramsecond units), 6




The Si Unit Of Gravitational Constant Is Youtube



1
G is the universal gravitational constant, usually taken as 6670 × 1011 m 3 / (kg) (s 2) or 6670 × 10 −8 in centimeter–gram–second unitsThe standard acceleration due to gravity (or standard acceleration of free fall), sometimes abbreviated as standard gravity, usually denoted by ɡ0 or ɡn, is the nominal gravitational acceleration of an object in a vacuum near the surface of the Earth It is defined by standard as 9806 65 m/s2 (about 05 ft/s2)Universal Gravitational Constant G The force of attraction between two objects with unit mass separated by a unit distance at any part of this universe Constant at any point in this universe G = 6673×1011 Nm 2 /kg 2 Nm 2 /kg 2




Gravitational Constant Wikipedia




Imgv2 1 F Scribdassets Com Img Document
Dictionary of physical constants, of the format physical_constants name = (value, unit, uncertainty) Available constants alpha particle mass e27 kg alpha particle mass energy equivalent e10 J alpha particle mass energy equivalent in MeV MeVN = kg m/s/s (in SI) From F = m a ;




Define Gravitational Constant Give Its Value Unit And Dimension Brainly In
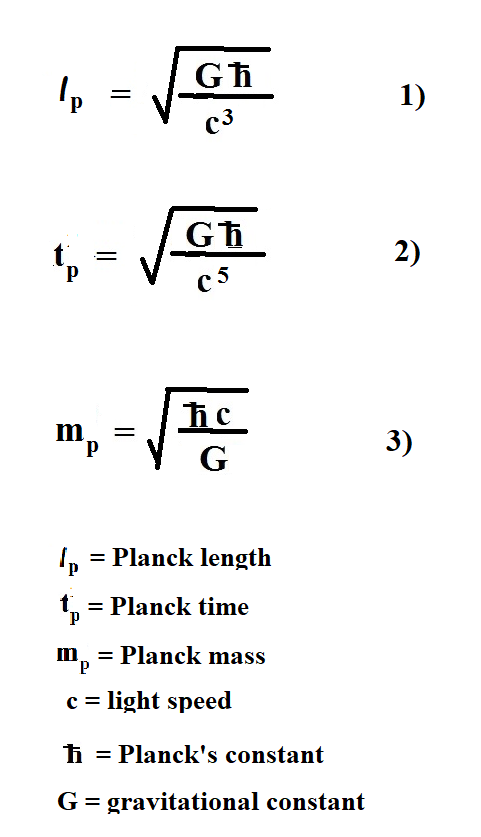



Gm Jackson Physics And Mathematics How The Gravitational Constant G Destroys Modern Physics



1




What Is The Si Unit Of G And G Teachoo Extra Questions




The Value Fo Universal Gravitationla Constant G In Cgs System Is 6 67xx10 8 Dyne Cm 2 Youtube




Newtons Universal Law Of Gravitation This Cartoon Mixes




Answered Newton S Law Of Universal Gravitation Bartleby
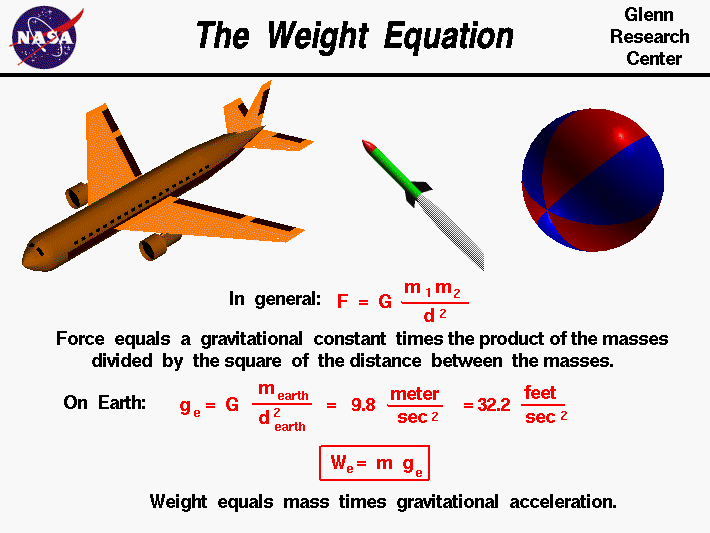



Weight Equation




10 X 2 1 State The Unit And Dimension Of Universal Gravitational Constant G



Newton S Law Of Universal Gravitation




7 The Universal Gravitational Constant Whose Chegg Com




C H A P T E R 4
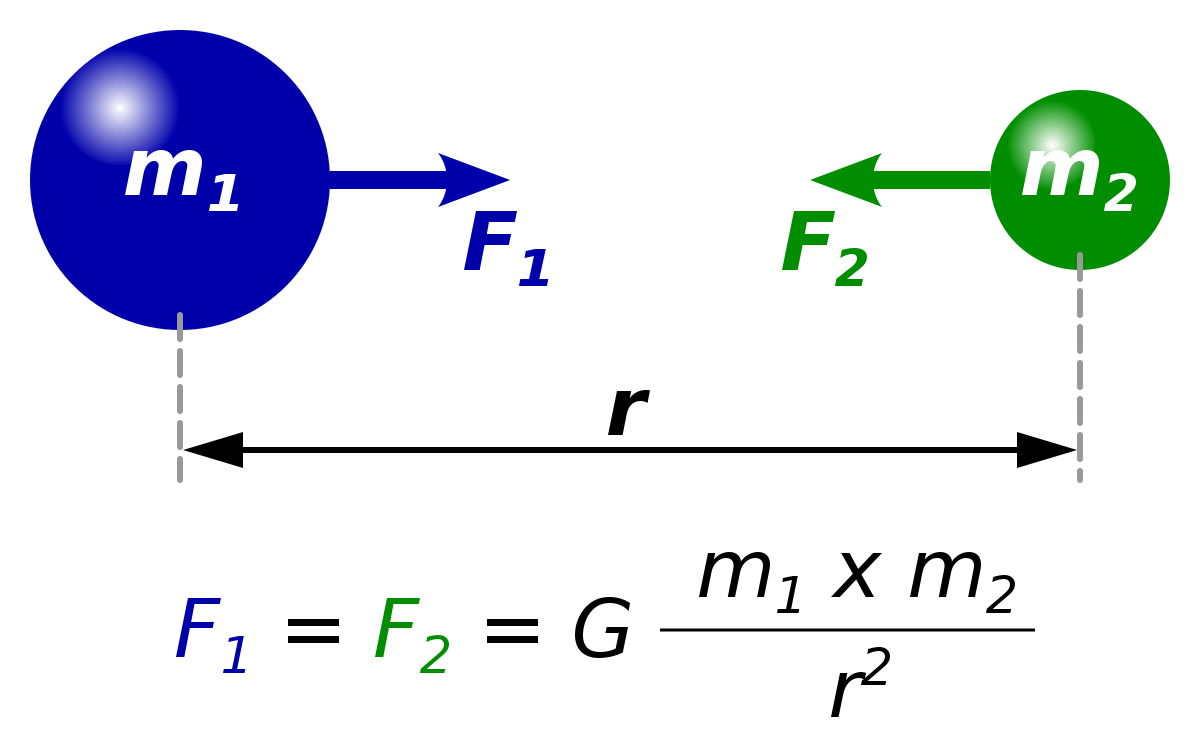



Gravitational Constant Wikipedia



1
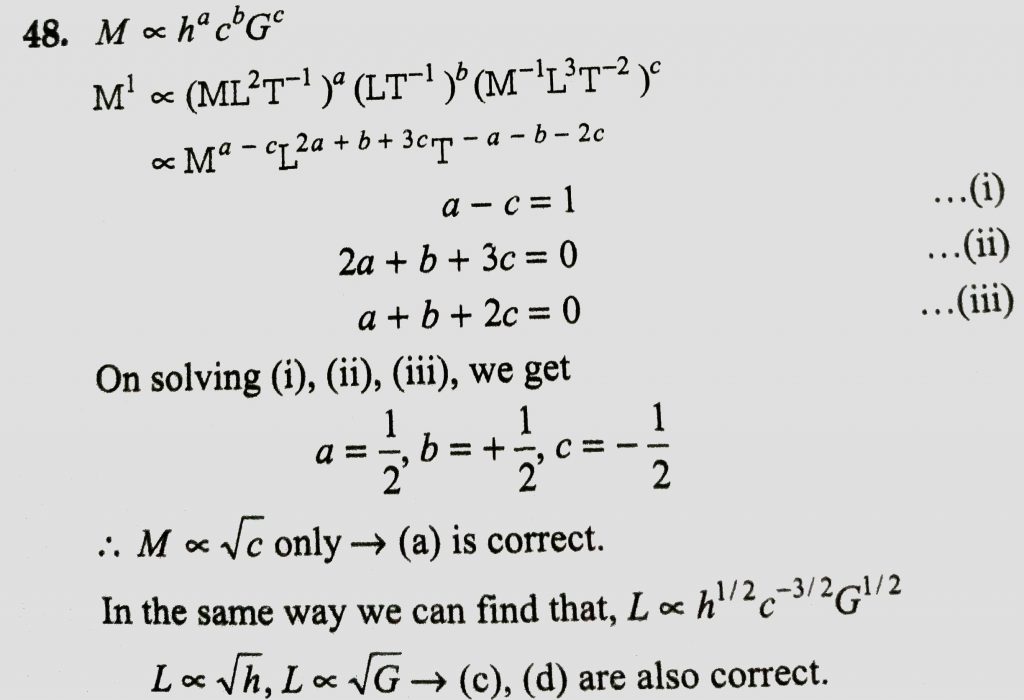



Planck S Constant H Speed Of Light C And Gravitational Constant G Are Used To Form A Unit Of Length L And Unit Of Mass M Then The Correct Options Is Are




Part Iii




S I Unit Of Universal Gravitational Constant G Is
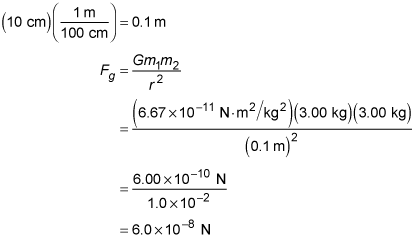



Gravitational Force In Physics Problems Dummies



The Most Accurate Value Of Gravitational Constant G Till Date




Convert The Value Of Universal Gravitationalconstant G From Si System To Cgs System Brainly In




Gravitational Force Overview Abstract By Mahmoud Nafousi Medium



Newton S Law Of Universal Gravitation



What Is The Unit And Cgs Unit Of Gravitational Force Quora
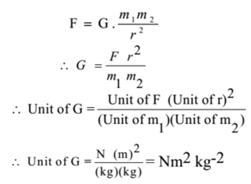



Newton S Law Of Gravitation Statement Explanation Problems




The Unit Of The Quantity G G Is Where G Is Gravitational Constant And G Is The Acceleration Due To Gravity A M Kg B Kg M C Kg M D None Of These
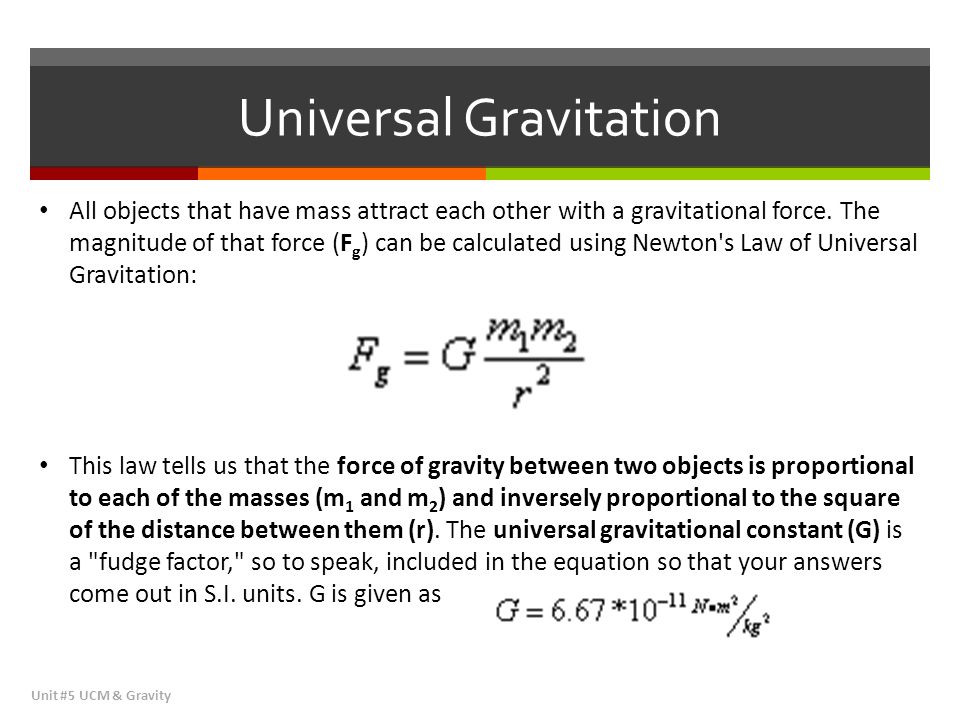



Ucm Gravity Gravity Unit 5 Ucm Gravity Ppt Download



1




The Universal Gravitational Constant Is G 66 74 Chegg Com




Abbreviations Symbols And Units G Universal Gravitational Constant Download Scientific Diagram




State Newton Law Of Gravitation Hence Define Universal Gravitational Constant G Give Value Of G In Brainly In



The Value Of Gravitational Constant Is 6 67 10 11 What Does It Mean Quora




The C G S Unit Of Universal Gravitational Constant Is Youtube




Gravitation Part 2 Video Khan Academy



What Is The Dimension Formula For A Gravitational Constant Quora




Gravitational Constant Ewt



Newton S Law Of Universal Gravitation
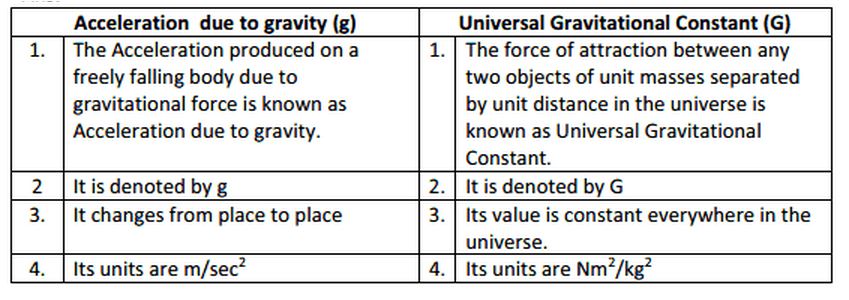



What Is Difference Between G And G Gravitation Science Class 9




What Are The Differences And Similarities Between Acceleration Due To Gravity G And Universal Gravitational Constant G Quora



What Are The Si Units For G The Universal Gravitational Constant Quora



If The Velocity Of Light C Gravitational Constant G And Planck S Constant H Are Chosen H As Fundamental Units What Are The Dimensions Of Mass Length And Time In The New System




Starting From The Given Attraction Force Equation Chegg Com




Color Online Six Components Of Fundamental Physical Constants G Is Download Scientific Diagram
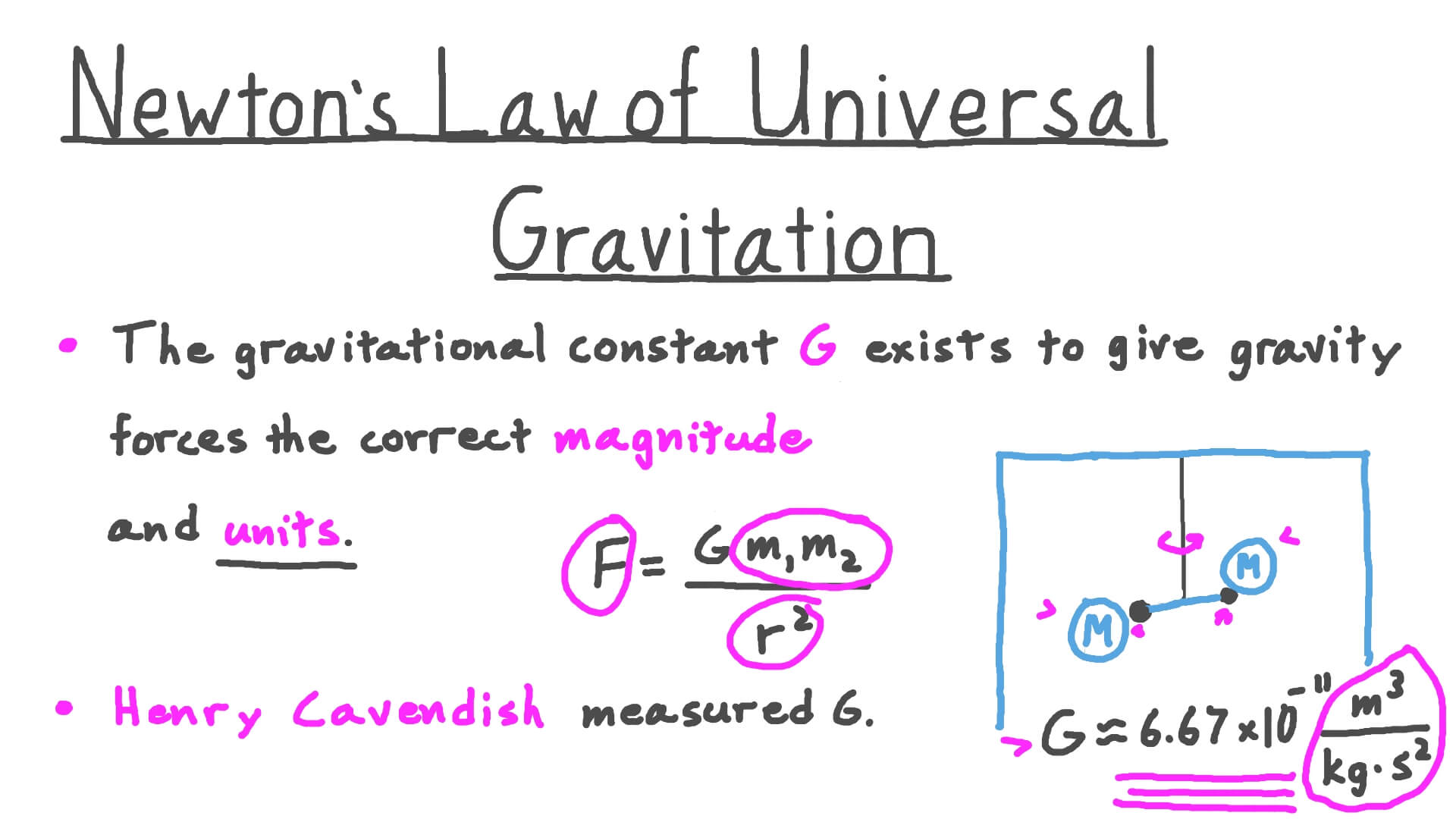



Lesson Video Newton S Law Of Universal Gravitation Nagwa
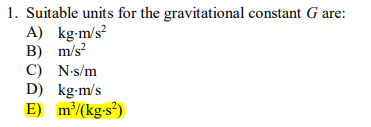



1 Suitable Units For The Gravitational Constant G Chegg Com




The Speed Of Light C Gravitational Constant G And Planc Scholr



If The Value Of Universal Gravitational Constant G Is 6 67 X 10 11 N M 2 Kg 2 In M K S System Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community




The Value Of Universal Gravitational Constant G 6 67xx10 11 Nm
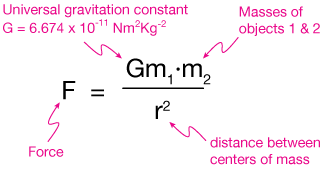



Gravity




Why Do Measurements Of The Gravitational Constant Vary So Much



What Is The Value Of Gravitational Constant G Quora




What Is The Gravitational Constant Universe Today




Gravitational Constant Is The G In Newton S Law Of Universal Gravitation Howstuffworks




Lakhmir Singh Physics Class 9 Solutions For Chapter 3 Gravitation Free Pdf




Unit 9 Department Of Physics Hku
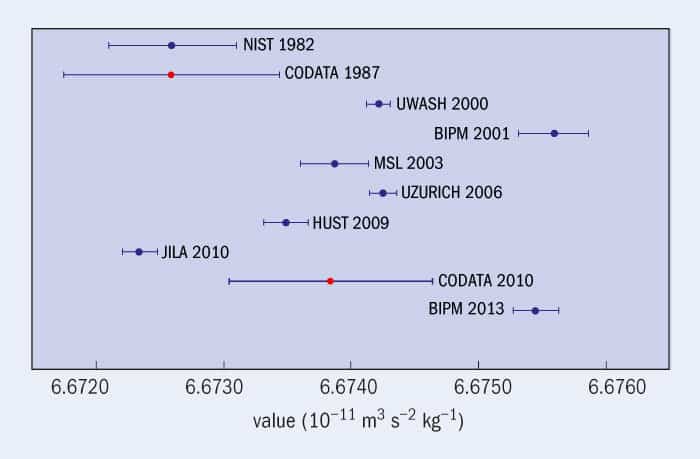



The Lure Of G Physics World




Universal Gravitational Constant An Overview Sciencedirect Topics




Sect 5 6 Newton S Universal Law Of Gravitation This Cartoon Mixes 2 Legends 1 The Legend Of Newton The Apple Gravity Which Led To Newton S Universal Ppt Download



Gravity Of Earth Units Of Measurement Wiki Fandom




Universal Gravitational Constant An Overview Sciencedirect Topics




Law Of Gravity




What Is The Si Unit Of G And G Teachoo Extra Questions
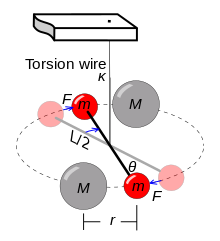



Gravitational Constant Wikipedia




If G Is Universal Gravitational Constant And G Is Acceleration




Introduction To Newton S Law Of Gravitation Video Khan Academy




Gravitational Constant Units Of Measurement Wiki Fandom




76 Planck S Constant H Speed Of Light C And Gravitational Constant G Are Used To Form Unit Of Length Physics Units And Measurements Meritnation Com




Derive Expression For Force Of Attraction Between Two Bodies And Then Define Gravitational Constant Cbse Class 9 Science Learn Cbse Forum




Invited Review Article Measurements Of The Newtonian Constant Of Gravitation G Review Of Scientific Instruments Vol No 11




Calculate The Dimensions Of Universal Gravitational Constant G What Is The Value Of G In Si Units Youtube




Newton S Universal Law Of Gravitation Physics




Define Universal Gravitational Constant Given Its Value With Si Units Youtube
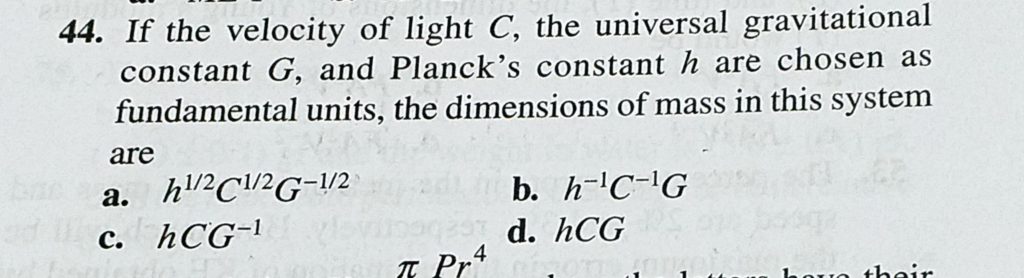



If The Velocity Of Light C The Universal Gravitational Constant G And Planck S Constant H Are Chosen As Fundamental Units The Dimensions Of Mass In This System Are Sahay Lms




Solved A Explain The Relationship Between The Universal Chegg Com



Gravity Of Earth




Two New Ways To Measure The Gravitational Constant




Question 1 6 Chapter One Measurements




A Suitable Unit For Gravitational Constant Is




Universal Gravitational Constant G 6 67 X 10 11 Chegg Com




What Is The Si Unit Of Gravitational Constant G Brainly In




1 Newton S Law Of Universal Gravitation Newton S



Gravitational Potential Energy



Gravitational Field Archives Page 2 Of 2 Regents Physics


コメント
コメントを投稿